First-time homebuyers in flood zones require flood insurance to protect against financial losses. The US is categorized into FEMA flood risk zones (A, B, C), with higher risks mandating stricter regulations and higher premiums. Traditional home insurance excludes flooding, making federal mandates crucial for protection. Coverage includes structures, belongings, and additional living expenses. Assess physical and climate factors for accurate risk evaluation. Understand policy types and use National Flood Insurance Program tools. Prompt claim notification and thorough documentation ensure fair resolutions. Underestimating flood insurance leaves buyers vulnerable to financial shocks from unforeseen events.
In a world increasingly shaped by unpredictable climate events, understanding flood insurance has become paramount for first-time homebuyers. Floods, once considered rare, are now frequent visitors to many communities, causing significant financial harm and disruption. Navigating the complex landscape of flood insurance can be daunting, with terms and policies that often seem like a foreign language. This clear guide aims to demystify flood insurance, providing an authoritative resource for first-time buyers to make informed decisions in the face of these growing risks. By the end, readers will possess the knowledge necessary to protect their investment and ensure peace of mind.
Understanding Flood Zones and Risks for Homebuyers

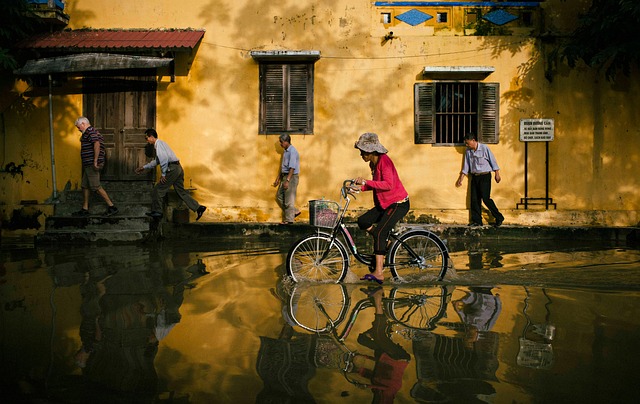
Understanding flood zones and associated risks is a crucial step for first-time homebuyers considering their need for flood insurance. The United States, with its diverse geography, experiences varying levels of flood risk, which is categorized into several zones by the Federal Emergency Management Agency (FEMA). These zones are based on historical data and flood studies, providing a clear indication of areas prone to flooding. Homebuyers must familiarize themselves with these zones, as they directly impact their insurance requirements.
Flood zones can be divided into three main categories: Zone A, Zone B, and Zone C. Zone A represents the highest risk, often referred to as Special Flood Hazard Areas (SFHAs), where flooding is considered an ongoing threat. Zones B and C have lower risks, but it’s important to note that even areas outside these designated zones can experience flooding due to various factors like heavy rainfall or storm surges. For instance, a study by the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA) revealed that nearly 20% of flood insurance claims are made in areas outside FEMA-designated high-risk zones. This underscores the importance of comprehensive risk assessment for all prospective homebuyers.
When considering purchase, borrowers should request and review their property’s flood zone designation through local government resources or online tools provided by FEMA. Based on this information, they can determine their flood insurance borrower requirements. Homeowners in higher-risk zones (like Zone A) may be subject to stricter regulations and higher premiums. However, purchasing flood insurance is not only a legal requirement in these areas but also a crucial step towards protecting one’s investment and ensuring financial security during unforeseen flooding events.
The Role of Flood Insurance: Protection and Coverage

Flood insurance plays a pivotal role for first-time homebuyers navigating the complexities of purchasing property in flood-prone areas. This type of coverage is designed to protect borrowers from significant financial losses resulting from flooding events. While it may seem like an additional expense, understanding the importance and scope of flood insurance is crucial for both peace of mind and ensuring one’s investment is secured.
In many regions, especially coastal or low-lying areas, homes are at risk of sudden and severe flooding due to storms, rising sea levels, or dam failures. Traditional home insurance policies typically do not cover these events, leaving homeowners vulnerable to substantial out-of-pocket expenses for repairs or even replacement of their property. Here’s where flood insurance borrower requirements come into play. Lenders often mandate flood insurance as a condition for providing mortgages in high-risk zones, safeguarding both the lender and the borrower. This is because flood damage can be extensive and costly, averaging over $30,000 per claim nationwide, according to recent data.
The coverage provided by flood insurance can include protection for your home structure, personal belongings, and even additional living expenses if you need to evacuate during a flood event. Policies may vary in terms of deductibles, coverage limits, and specific exclusions, so borrowers should carefully review their policy details. It’s essential to understand the potential risks associated with living in these areas and select a flood insurance plan that aligns with those needs. By taking this proactive step, first-time homebuyers can safeguard their largest investment and prepare for unexpected natural events.
Evaluating Your Property's Vulnerability to Flooding
Evaluating your property’s vulnerability to flooding is a crucial step in understanding your need for flood insurance as a first-time buyer. This process involves assessing both physical factors and environmental conditions that contribute to potential risk. For instance, properties located in low-lying areas, near rivers or coastal zones, or with poor drainage are more susceptible to flooding events. According to the Federal Emergency Management Agency (FEMA), over 90% of all natural disasters in the U.S. involve some form of flooding, underscoring the significance of this risk assessment.
To gauge vulnerability, examine your property’s topography and surrounding landscape. Are there any historical data or community reports of past flooding incidents? Check with local authorities or neighborhood associations for insights into previous flood events. Additionally, consider the type of construction and infrastructure on your property. Older homes might lack modern drainage systems or be built to less stringent codes, potentially increasing vulnerability. By understanding these aspects, you can better determine if your property falls within the high-risk categories that typically require specific flood insurance borrower requirements.
Further, it’s essential to account for climate change impacts. Rising sea levels and increased rainfall patterns are altering flood risk landscapes nationwide. Data from the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA) indicates that severe weather events have intensified over the past few decades, leading to more frequent and severe flooding episodes. This changing environment necessitates a proactive approach to evaluating flood risks, ensuring you’re adequately insured. Regularly updating your assessment as environmental conditions evolve is key in staying protected under the right flood insurance policies.
Choosing the Right Flood Insurance Policy

Choosing the right flood insurance policy is a crucial step for first-time homebuyers. As flood events become more frequent and severe due to climate change, securing adequate coverage is essential to protect your investment and ensure peace of mind. One key aspect to consider is understanding the different types of policies available and tailoring them to your specific location and risk level.
Flood insurance borrower requirements vary based on factors such as the flood zone classification of your property and the value of your home and belongings. The National Flood Insurance Program (NFIP) offers two primary coverage options: Standard Flood Insurance Policy (SFIP) and Flood Insurance Policy (FIP). The SFIP provides coverage for physical damage to buildings and possessions, while the FIP includes additional living expenses if you need to evacuate your home due to a flood. It’s important to evaluate these options based on your individual needs and risk assessment.
For instance, borrowers in high-risk areas might require a more comprehensive policy that covers higher levels of damage and additional living expenses. Conversely, those in lower-risk zones may opt for a basic policy with lower coverage limits. The NFIP provides valuable tools to help homeowners determine their specific flood insurance borrower requirements. By considering these factors and comparing different policies, you can make an informed decision, ensuring your investment is adequately protected against the potential devastation of a flooding event.
Claim Process: Navigating Post-Flood Recovery

Navigating post-flood recovery is a complex process, especially for first-time flood insurance buyers. Understanding the claim process is a crucial step in this journey. Flood insurance, designed to protect homeowners and businesses from financial loss due to flooding, plays a vital role in this recovery narrative. When a flood occurs, borrowers with comprehensive flood insurance can expect a structured claims process that aids in their recovery efforts.
The initial step involves contacting your insurance provider as soon as possible after the flood. Most policies require prompt notification to ensure a smooth claims journey. Borrowers should then document the damage meticulously, taking photos and keeping records of all expenses related to the flood. This evidence is crucial for verifying the extent of the loss during the claim assessment phase. According to recent studies, timely filing and comprehensive documentation significantly impact the speed and amount of insurance claims settled.
After submitting your claim, the insurance company will inspect the property and assess the damage. They may also require additional information or documents to support your claim. During this period, maintaining open communication with your insurer is essential. Once the assessment is complete, the insurance company will provide a settlement offer based on the policy terms and the repair estimates. Borrowers should carefully review the offer, ensuring it aligns with their expectations and the actual repair costs. This step emphasizes the importance of understanding flood insurance borrower requirements to ensure a fair claim resolution.
Common Mistakes First-Time Buyers Should Avoid

First-time homebuyers often face a host of challenges, and navigating flood insurance is no exception. This critical aspect of homeownership can be particularly daunting, given the unique borrower requirements and potential for costly mistakes. Many first-time buyers overlook the significance of flood insurance, assuming it’s only relevant in low-risk areas or for properties with historical flooding issues. However, this oversight can lead to severe financial consequences post-purchase. For instance, a sudden change in weather patterns or an unforeseen shift in local topography could render a seemingly safe property vulnerable to flooding, leaving the new owner responsible for substantial repair bills and potentially even relocation costs.
Avoiding common pitfalls is key to ensuring a smooth transition into homeownership. One of the primary mistakes first-time buyers make is assuming their regular homeowners insurance policy covers flooding. While standard policies typically exclude flood damage, there are specific flood insurance products designed to fill these gaps. These policies are essential for anyone living in an area prone to flooding, as defined by federal standards based on historical data and risk assessments. Understanding these borrower requirements is crucial; failure to acquire appropriate coverage can result in denial of future claims or significantly delayed settlements.
Further, buyers should scrutinize their property’s location and proximity to water sources. Even properties far from visible bodies of water may be at risk due to changing weather patterns and urban development. Researching local flood maps and consulting with insurance professionals can provide valuable insights into specific risks. By being proactive and informed, first-time buyers can safeguard their investments and avoid the financial shocks that often accompany unexpected flooding events.














