Flood insurance is mandatory for first-time homebuyers in high-risk U.S. counties, protecting against damage not covered by standard home insurance. National Flood Insurance Program (NFIP) risk assessments determine coverage requirements based on local flood trends and environmental factors. Policies vary in scope and deductibles; understanding these terms ensures adequate protection. Consulting experts and using NFIP mapping tools aids in selecting appropriate coverage. Regular policy updates are essential as home values and locations change, offering peace of mind against escalating climate-related risks.
In a world where natural disasters can strike with unpredictable ferocity, ensuring adequate protection for your property is paramount, especially against the relentless forces of flooding. For first-time homebuyers, navigating the complex landscape of flood insurance can be daunting. This comprehensive guide aims to demystify the process, providing a clear roadmap to help you make informed decisions. We’ll delve into the significance of flood insurance, clarify common misconceptions, and offer expert insights tailored for those new to this essential coverage. By the end, you’ll be equipped with the knowledge to protect your investment wisely.
Understanding Flood Insurance Basics: What You Need to Know

Flood insurance is an essential consideration for any homeowner, but it’s especially critical for first-time buyers navigating the complexities of homeownership. Understanding flood insurance basics involves recognizing both its necessity and the unique borrower requirements it entails. According to the National Flood Insurance Program (NFIP), over 90% of U.S. counties have at least some risk of flooding, making flood insurance not a luxury but a necessity for many.
One of the primary aspects to grasp is that standard home insurance policies typically do not cover flood damage. This gap in coverage highlights the need for separate flood insurance, which is designed to protect homeowners and their investments from the devastating effects of floods. Flood insurance borrower requirements include meeting specific criteria set by the NFIP, such as living in a designated flood zone and ensuring your property complies with flood-resistant construction standards. Failure to meet these requirements can result in denied claims or higher premiums.
For first-time buyers, it’s crucial to factor in potential flood risks when considering a home purchase. Checking the Flood Map (also known as the National Flood Risk Layer) provided by the NFIP is an excellent starting point. This resource offers detailed information on flood zones and can help you identify high-risk areas. Additionally, engaging with a real estate agent or lender who has experience in flood insurance can provide valuable insights into the local market dynamics and potential borrower requirements.
Beyond compliance, understanding your policy terms is vital. Flood insurance policies vary in coverage amounts, deductibles, and exclusions. Familiarize yourself with these details to ensure you have adequate protection for your property. Remember that while flood insurance offers peace of mind, it’s just one component of a comprehensive risk management strategy for homeowners. By proactively addressing flood insurance borrower requirements and understanding policy specifics, first-time buyers can mitigate risks and protect their investments in an often unpredictable natural environment.
Evaluating Your Risk: Assessing Flood Potential as a Buyer
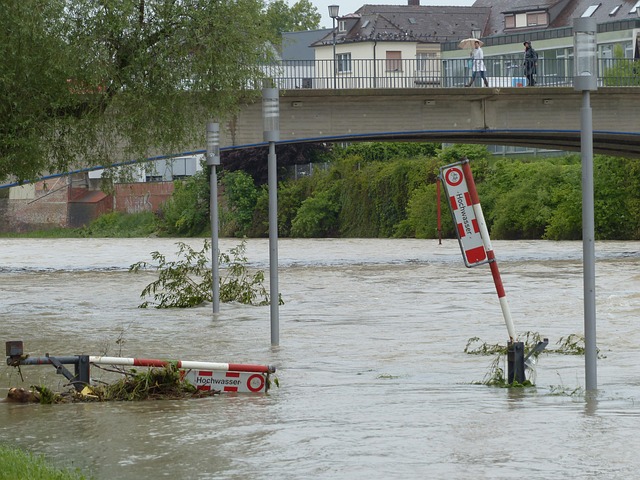

When considering a home purchase, especially in areas prone to flooding, evaluating your risk is paramount. Understanding flood insurance—its purpose, requirements, and cost—is crucial for any first-time buyer. Flood insurance isn’t just about protecting your asset; it’s a necessary step for qualifying as a borrower in many high-risk zones.
Risk assessment begins with a thorough understanding of local flood trends. According to the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA), almost 20% of the U.S. population lives in areas at risk of flooding, with that number increasing annually due to climate change. Your potential for exposure varies based on location, past events, and environmental factors like topography. For instance, living near a river or on a slope increases your vulnerability. Historical data can guide this assessment; review local records to see how often and severely floods have impacted your desired neighborhood.
Identifying your specific risk level is the first step in navigating flood insurance borrower requirements. Lenders typically demand proof of flood insurance coverage for properties in high-risk areas, as outlined by the Federal Emergency Management Agency (FEMA). This protection is usually through a policy from a private insurer, not a government program. Policy costs vary based on your risk profile; factors like property value, location, and flood history influence premiums. As a borrower, you’ll need to secure sufficient coverage that aligns with your specific risk assessment—a process made easier by consulting with experts and utilizing available resources, such as FEMA’s mapping tools.
Navigating the Process: Getting and Using Flood Insurance Effectively

Navigating the process of obtaining and utilizing flood insurance effectively is crucial for first-time homebuyers, especially given the increasing frequency and intensity of extreme weather events. As climate change takes hold, understanding your obligations as a borrower in high-risk areas becomes paramount. Flood insurance isn’t just an optional add-on; it’s a necessary safeguard against potential financial ruin caused by devastating floods.
The first step in navigating this process involves assessing your specific risk level through the National Flood Insurance Program (NFIP). This federal program provides standardized flood maps and data, enabling you to determine if your property falls within a Special Flood Hazard Area (SFHA) or has a lower risk profile. Once identified, borrowers in high-risk zones are typically required to purchase flood insurance as a condition of their mortgage. Lenders will usually provide details on the minimum coverage levels mandated by law and guide you through the selection of an appropriate policy.
Beyond meeting borrower requirements, smart homeowners go beyond the bare minimum. They carefully review their policy’s scope of coverage, understanding what’s included and excluded. For instance, standard policies often exclude basement flooding unless a separate rider is purchased. These riders can expand coverage to include specific perils like burst pipes or heavy rain. Regularly updating your flood insurance policy based on changes in your home’s value or location ensures adequate protection. Remember, the right flood insurance isn’t just about meeting obligations; it’s about securing peace of mind and financial resilience in the face of an ever-changing climate.